5D Meshing operation
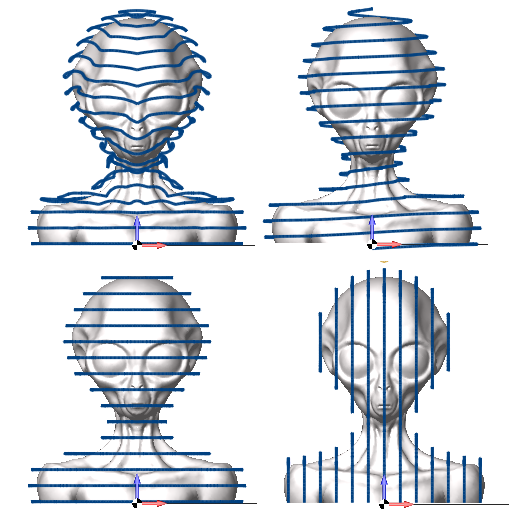
Overview
A versatile 5 axis finishing operation with a powerful set of strategies, tool axis orientation modes and automatic tool and holder collision avoidance. Perfect for finishing of complex shapes such as sculptures or scanned STL models. Easy to use.
The operation allows machining mesh models similarly to Scallop finishing operation, Helical operation and Waterline strategy from 5d surfacing operation. The operation allows generating machining toolpath on the 5 axis machines.
For setting spherical tool normals the 5 axis tool path conversion option is available.
Supported model types
Surface models
Triangular mesh models
Supported tool types
Spherical mill
Conical mill with a spherical end
Lollipop mill
Strategies
Scallop
Helical
Waterline
Plane
Tool axis orientation modes
Fixed
Normal to Surface
To Rotary Axis
To/From Curve
To/From Point
Perpendicular to Toolpath
Job assignment
Faces of the part
Job Zones
Start Curves
Quick start
Just create the operation and press Run. The operation will generate a scallop pattern on the whole part starting from the bottom level. The tool will stay in the vertical orientation unless there is a collision with the part, otherwise it will be tilted to the side.
Workflow
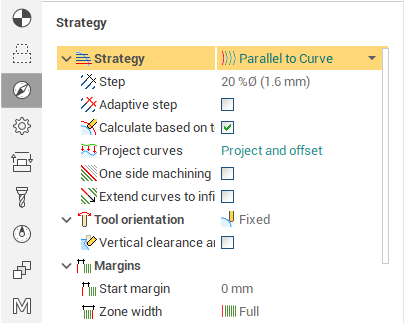
Define the toolpath Strategy. The default strategy is Scallop as it allows to machine the whole part with a consistent stepover.
Choose the tool axis orientation. The default option is Fixed, because together with the automatic collision avoidance it doesn't require any additional setup and achieves a smooth and predictable toolpath.
Define the collision avoidance strategy. The default is Side Tilting, as it is works well with Scallop, Helical and Waterline patterns.
Optionally, define the job zone
Generate the toolpath